Some of the links on our website are affiliate. By making a purchace via our links, you help us create new content and support animal shelters and funds
Rabbit life cycle
Rabbits are cute little animals and are occasionally kept as pets. Domesticated rabbits may live a decade or longer, and you need to pay attention to their needs during different stages of their life.
A newborn bunny requires different care compared to an adult rabbit. So here is a closer look at the pet rabbit life stages.
Bunny life stages
Here are the four main stages of the rabbit’s life cycle:
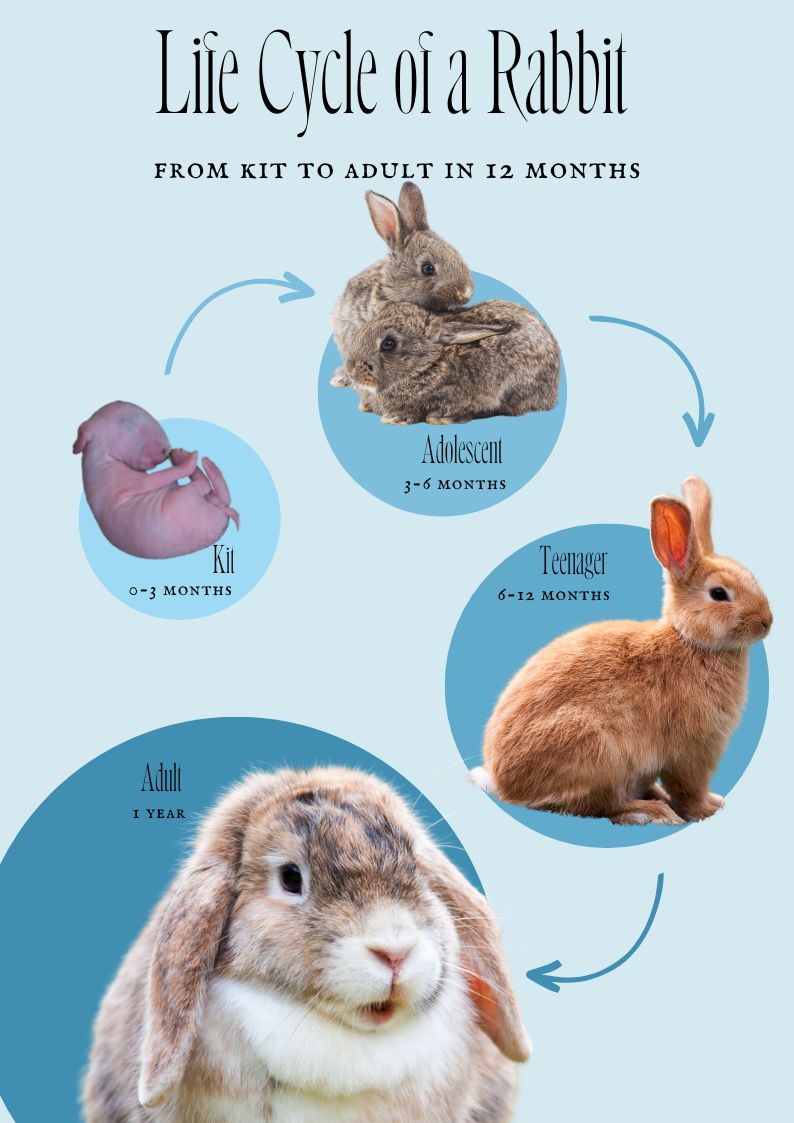
The life cycle of a rabbit includes several stages as they mature from newborns to adults. Rabbits are often referred to as kits from the time when they are born until they mature. Kits can also be divided into newborns, adolescents, and teenagers.
The diet and care of a rabbit depend on its current stage of development.
Read on to learn all you should know about rabbit's life cycle, and we'll start from the very begging - gestation.
Gestation
The gestation period for rabbits is about 31 to 33 days. At about 12 days, you may be able to feel the growing bump in the rabbit’s belly.
Several days before giving birth, mother rabbit builds a nest. Rabbits also pull their own fur to line the nest and keep the newborns warm.
The average size of a litter is five bunnies. However, some mothers may give birth ("kindle") to just one rabbit while others have as many as 12 newborns. Larger breeds of rabbits tend to have larger litters while smaller breeds may have just one to three kits per litter.
After the delivery, mother rabbit cleans up by eating the placenta and membranes.
Newborn bunny

Newborn bunnies are called kittens and kits. The newborn stage is the most crucial for the survival of a young rabbit.
The average size of a newborn bunny is a little under 2 inches in length with a weight of 30 to 35 grams. They are also born blind and without hair.
Newborn kits cannot regulate their body heat for the first week. Their hairless bodies need warmth and milk.
In rare cases, a mother rabbit may eat her young. This is more likely to occur when the mother is frightened or panicked after birthing the litter.
Some newborn bunnies also struggle to obtain enough nutrition during the first few weeks, especially in a large litter. If you are caring for a new litter, make sure that each kitten receives the milk that it needs.

Baby bunnies start growing soft fur almost immediately. They open their eyes around 7th-10th day after birth, grow enough fur to stay warm by day 9, and can move their ears around the 12th day.
Rabbits are weaned from their mother’s milk at around three to five weeks of age. They are no longer newborns but are still referred to as kittens or kits until they reach adolescence.
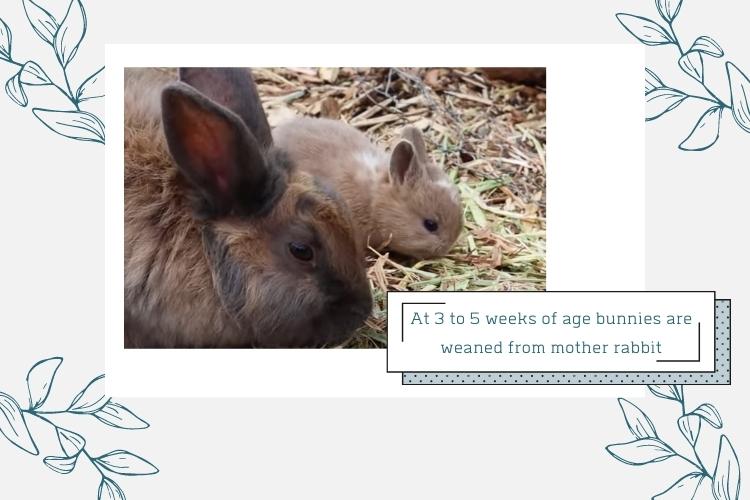
Breeders may give newborns Alfalfa hay at around three weeks of age to encourage the weaning process. At four to six weeks of age, rabbits are aware of their surroundings and start nibbling on solid foods, including hay.
Watch the baby rabbits grow in this time-lapse video from day 1 to day 30:
Pet rabbits are often sold when they are at least eight weeks old. At this point, rabbits are fully weaned and eating solid foods.
Interestingly, it's in the Newborn stage that it's the easiest to tell the age of a bunny.
Adolescent rabbit

Rabbits are considered adolescents when they reach sexual maturity, which occurs when they are about three to four months old.
Wild rabbits start breeding as soon as they are sexually mature. Some female rabbits may even give birth to a litter during the same season that they were born. However, domestic rabbits should not start breeding until at least the age of six months.
Waiting a couple of extra months ensures that the rabbit is more fully developed, which can decrease the risk of complications when giving birth.
Teenage rabbit
The teenage stage is not widely recognized as part of the rabbit’s life cycle. However, many rabbit owners notice changes in behavior as the rabbit transitions from adolescence into adulthood.
After a rabbit sexually matures, but before its first birthday, it may go through a period of moodiness. As with human teenagers, teenage rabbits may exhibit unusual behavior. Examples include potty accidents, spraying urine, teeth grinding, and aggression.
Adult rabbit
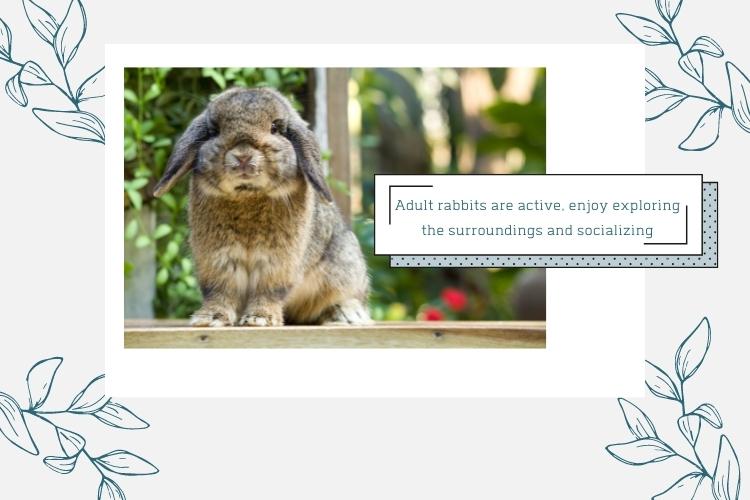
Rabbits are typically considered adults at about 12 months of age. The young adult stage lasts until the rabbit’s third birthday. Young adult rabbits are fully mature but no longer suffer from the moodiness that occurs earlier.
Young rabbits are very active. They enjoy exploring their environments and socializing with other rabbits.
At about three years of age, most rabbits start slowing down. They become less active. You may also notice that your pet rabbit gradually becomes more affectionate.
During your rabbit's middle-aged years, you should think about taking it to the vet twice per year. Rabbits are more likely to develop health problems as they age.
Instead of running around exploring, your rabbit may prefer sitting in the same room as you. At about six to seven years of age, rabbits are considered old. They may eat less and become much calmer compared to their earlier years.
Rabbit life cycle FAQ
How many stages are there in the life cycle of a rabbit?
During their life cycle, rabbits go through four main life stages: newborns (0 to 3 months), adolescents (3 to 6 months), teenagers (6 to 12 months), and adults (1 year and older). We could also distinguish a senior rabbit life stage, which starts at about 6 to 7 years of age.
How long is rabbit life cycle?
Domesticated rabbits can live from 8 to 12 years. As opposed to their wild relatives, who typically live one to two years on average.
When do rabbits become adults?
Rabbits are considered adults as they reach the age of 1 year old. But, depending on rabbit breed, some may still grow and reach their adult size by the age of 14-18 months.

